The ultra sensitive GOCE Accelerometers and their future developments
Jean-Pierre Marque (*), Mr. Bruno Christophe, Dr. Bernard Foulon, Mr. Pierre Touboul
Office National d’Etudes et de Recherches Aérospatiales (ONERA), 29 Avenue de la Division Leclerc, BP-72, 92322 Châtillon, France
(*) Jean-Pierre.Marque@onera.fr
By combining satellite Gradiometry with SST-high-low GPS tracking, the ESA GOCE
mission aims to provide a high resolution Gravity Field to the Scientific and Engineering
communities. Continuous 3D GPS tracking of the satellite and compensation of nongravitational
forces, thanks to on–board accelerometers, open the way to the fine measurement
of gravitational gradients at the gradiometer location, at a steady low altitude.
The tri-axes Gradiometer is conceived around six electrostatic accelerometers which are
organised in three orthogonal pairs. The accelerometers were specifically developed to
guarantee a level of noise acceleration as low as 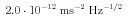 , for a measurement range
of
, for a measurement range
of 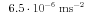 .
.
They are based on a similar principle than the ones embarked on GRACE twin satellites but with some design and technical evolution to improve their resolution by two orders of magnitude and to satisfy the specific gradiometric requirements.
Their contributions to the mission is double by providing, on one side, the drag-free and attitude control system with the linear accelerations of the satellite and, on the other side, by delivering the scientific data to be on-ground processed to extract the GGT components. The GOCE satellite was launched on March 17, 2009 from Plessetsk in Russia and the Gradiometer was switched on the 8 of April 2009, in science mode.
The paper will present the main characteristics of the accelerometers and the preliminary data, obtained after the first months in orbit, illustrating the in-flight behaviour of the six accelerometers. The future accelerometer developments for the gravity mission of the next generation will be presented focusing on trade-offs betweens sensors, satellite requirements and in orbit configuration.
The accelerometers of the GOCE mission have been developed by ONERA under contract with ESA through Thales Alenia Space as Prime Contractor of the mission.